Are you a manufacturing company concerned about the decision to choose a 3D printing technology that is best for your project? 3D printing has completely changed prototyping and manufacturing due to its efficient capability to create designs. The extensive growth and comprehensive service capabilities of 3D printing solutions aim to fulfill every requirement from prototype development to miniature production and final industrial product manufacturing.
However, it is not easy to select a tailored 3D printing technology that meets your project needs because numerous options are available in the market. The life-like representations of your ideas come from 3D printing services based on SLA, DLP, FDM, and SLS printing systems technologies. The evaluation of such technologies to find the best one for your needs helps you increase production efficiency, minimize expenses, and implement advanced design concepts for your business operations.
3D printing technologies like Stereolithography (SLA) and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) are quite useful in providing benefits and custom solutions for their users. In this post we are focusing on SLA and FDM technologies. Let’s understand SLA and FDM 3D Printing, and the difference between these technologies to recognize the best one for your particular needs.
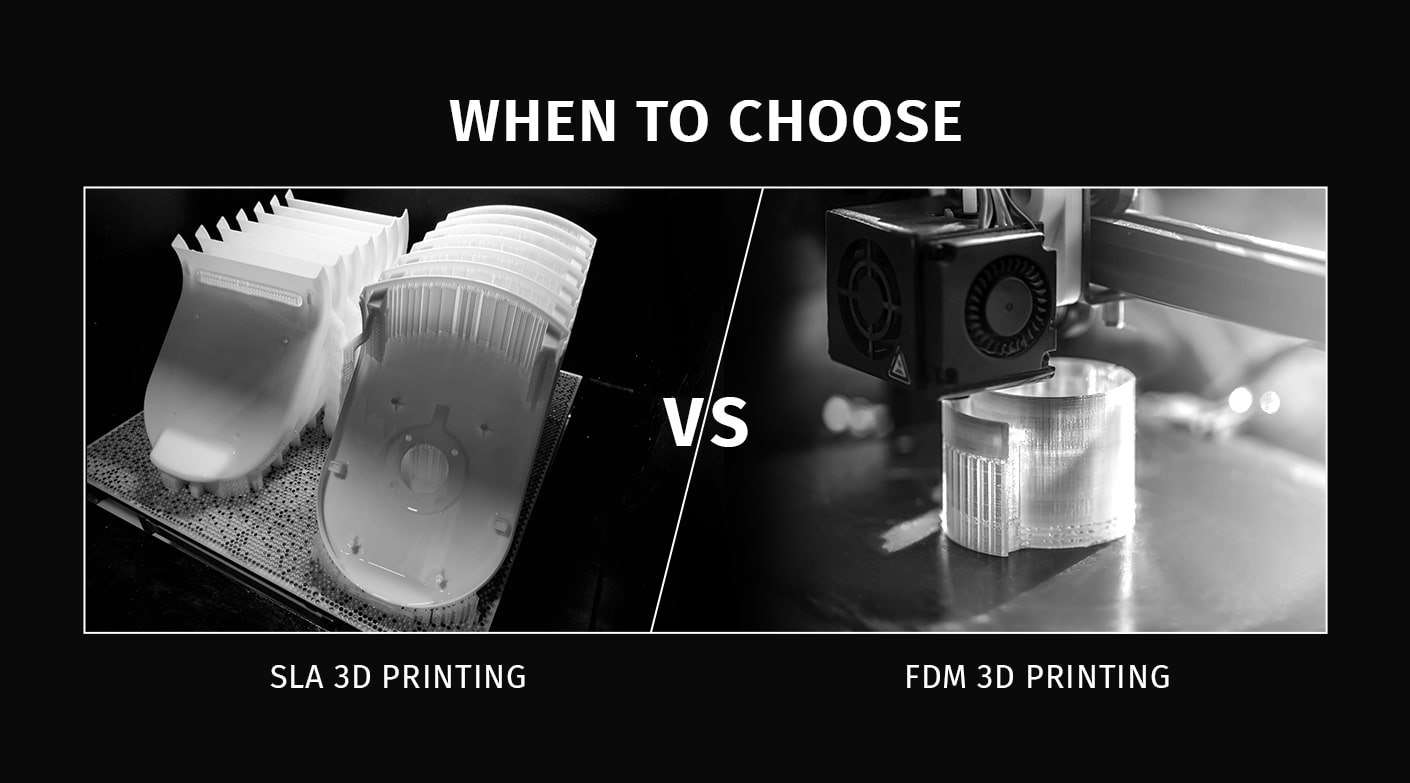
SLA 3D Printing vs FDM 3D Printing
What is SLA 3D Printing?
SLA 3D printing is a resin-based rapid prototyping method that stimulates liquid photopolymer resin with a laser beam to form precise layers, which leads to smooth finished parts. SLA printers selectively cure layers of resin one by one.
Through the printing methodology, the construction of SLA parts maintains few layer lines, which results in better surface quality. The resin-based technology of SLA 3D printing shapes detailed and polished parts through successive laser curing of liquid photopolymer resin. This technology is used in areas which need precise manufacturing and smooth outer surfaces.
Which Manufacturing Problem SLA Solves?
- SLA is different from FDM because FDM uses plastic filament through extrusion but SLA builds accurate complex details by curing light-sensitive resin. SLA is used in various items such as dental, jewelry, healthcare equipment, and prototyping.
- The manufacturing capabilities of SLA extend to transparent model production that is used in different industrial sectors. Industries seeking precise, accurate details should opt for SLA because of its exceptional capabilities.
- SLA 3D printing offers manufacturers the advantage of delivering high-end parts with low visible layer lines and smooth surfaces.
- The curing process of selective resin layers takes place through either a laser or digital light processing system, which ensures superior surface quality when compared to FDM.
- The industrial applications of SLA include a wide range of specialized resins, as well as flexible and biocompatible options for various purposes.
Limitations of SLA:
- Developing prototypes from SLA includes different supplementary stages of washing with UV curing followed by support removal to reach ideal mechanical properties.
- The detailed parts delivered by SLA result in lengthy manufacturing durations and complex production processes, therefore minimizing their speed for high-volume manufacturing needs.
What is FDM 3D Printing?
FDM 3D printing stands out as one of the most common rapid prototyping techniques to produce object layers sequentially from thermoplastic materials. A FDM printer uses heated nozzles to extrude thermoplastic filaments having materials like ABS, PLA, PETG, and nylon.
The thermoplastic material becomes liquid because of the heating process that occurs before it solidifies on the print bed. The printer applies repeated material layers until the desired object is printed. Due to printer settings, the resulting objects may display different degrees of detail along with different amounts of mechanical strength.
Which Manufacturing Problem FDM Solves?
- Using FDM printers, manufacturers get access to diverse materials suitable for manufacturing processes.
- Manufacturers can create pieces that require diverse mechanical characteristics because the technology operates with numerous flexible and reinforced composite thermoplastics.
- The technique became popular for manufacturers because it offers low costs, easy access, and user-friendly operations.
- The ability to work with various plastic materials makes FDM a suitable technology for producing functional prototypes along with mechanical components.
- The scalability of FDM technology allows manufacturers to produce big objects at a reduced manufacturing expense in comparison to other 3D printing solutions.
Limitations of FDM:
- FDM technology delivers limited resolution quality and coarse finishing characteristics than what SLA produces.
- Manufacturers need to use sanding, together with chemical smoothening and painting, to improve visual appearance.
When to Choose SLA vs FDM 3D Printing?
| SLA 3D Printing | FDM 3D Printing | |
| Material Used | Liquid photopolymer resin | Thermoplastic filament |
| Print Quality | High resolution, smooth surface finish | Lower resolution, visible layer lines |
| Strength | Brittle but highly detailed | Strong and durable |
| Cost | Higher material and machine costs | More affordable |
| Ideal for | Dental, jewelry, medical, prototypes | Large parts, functional prototypes |
| Post-processing | Requires washing, UV curing | Object perfection may require sanding treatment and chemical smoothing procedures. |
| Print Speed | The cure duration extends because of a detailed curing process. | Generally faster |
| Part Size | Best for small to medium-sized objects | Can produce large objects affordably |
For High-Detail and Smooth Finishes – Choose SLA
SLA provides better results when your project requires high levels of precision and a smooth surface finish. The material works best for dental models, jewelry products, as well as aesthetic prototypes because of its ideal properties.
For Affordable prototyping – Choose FDM
The FDM technology stands out as the economic solution for big functional and mechanical components, which makes it ideal for concept modeling programs.
For Strength and Durability – Choose FDM
To manufacture engineering prototypes and end-use products that need impact resistance as well as toughness, FDM thermoplastic filaments deliver the best strength properties.
For Medical and Engineering Precision – Choose SLA
The medical field, healthcare, and precision engineering use SLA technology to fabricate detailed models which show minimal dimensional flaws.
For Large Parts – Choose FDM
As FDM printers manage to produce larger object sizes than SLA printers, they become perfect for automotive, aerospace industries and massive industrial components production.
Conclusion
The future projection for the global 3D printing service market is 37.2 billion U.S. Dollars in 2026. This huge potential means investing in any 3D printing tech for product manufacturing will be rewarding. However, considering the availability of numerous 3D printing technologies, the selection of the most suitable 3D Printing for your project depends on your project requirements.
The best option for projects that require precise details as well as smooth finishes is SLA systems. The decision favors FDM when considering reduced costs, longer material lifespan, and ability to scale.
However, if you need a guided approach to select the best 3D printing services for your needs or want to zero down between SLA vs. FDM, then Cubein experts are here to help. At Cubein, our professional 3D Printing services in India serve businesses for realizing their concepts through appropriate 3D printing technologies. Through the Custom Prototyping & Design Services, Cubein provides customized 3D solutions to businesses.
If you are seeking expert 3D Printing services for your next project? Contact us now!