In today’s fast-paced world, bringing an idea to life quickly and efficiently is crucial for success. Enter rapid prototyping, a method that allows businesses and innovators to create a tangible model of their concept swiftly. While the concept of rapid prototyping sounds straightforward, there are crucial factors to consider to ensure you reap the benefits.
Let’s dive into the types of rapid prototyping and the key factors that can make or break your rapid prototyping journey.
Know the basics of Rapid Prototyping, first:
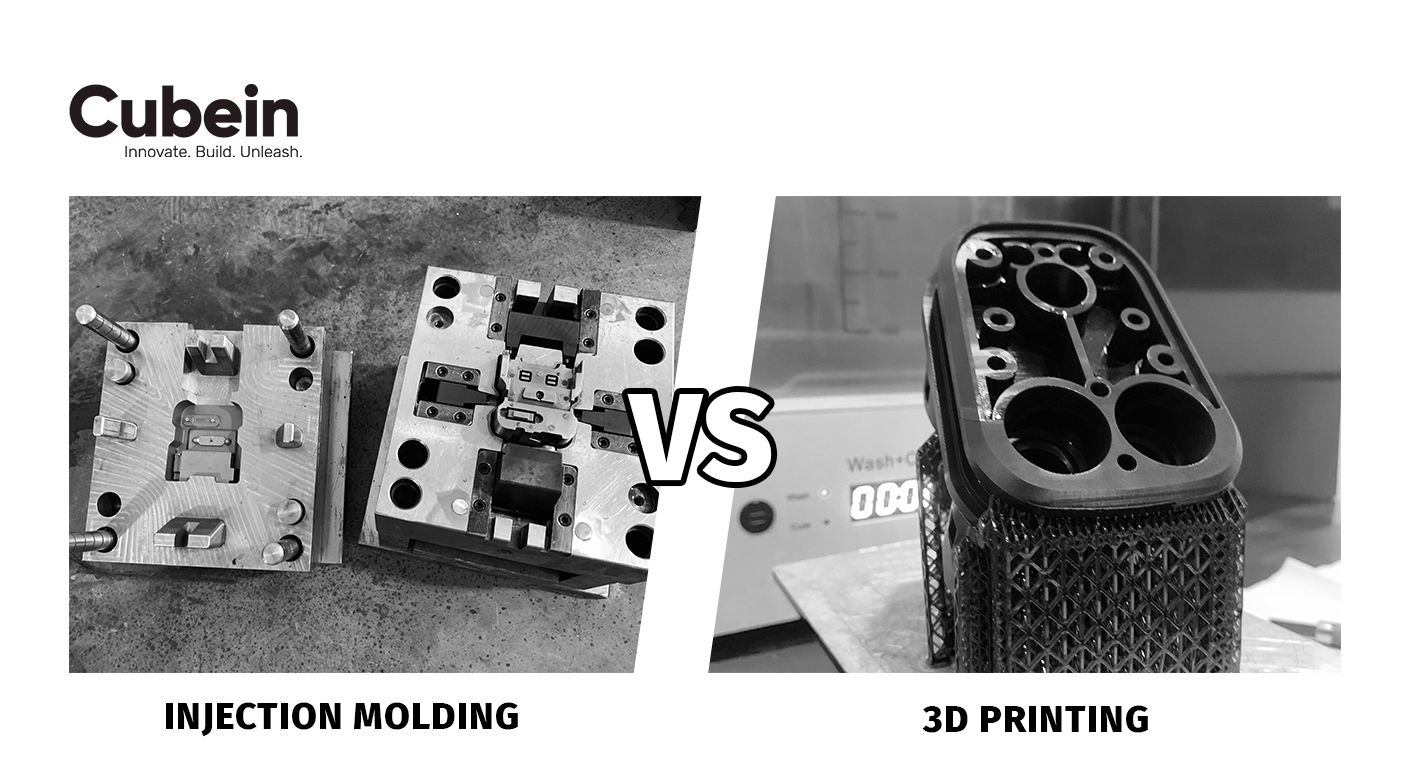
Rapid Prototyping is a group of technologies used to fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly quickly with the use of three-dimensional computer-aided design or CAD data. The assembly or the construction of the part is usually done by using 3D printing or Additive Layer Manufacturing technology.
Types of Rapid Prototyping:
There are various types of rapid prototyping. Here are some of them:
1. Selective Laser Sintering:
Selective Laser Sintering or SLS is an additive manufacturing technology, which uses a high-power laser to solidify a structure from sintered small particles of polymer powder, based on a 3D model.
2. 3D printing:
3D Printing is a process of making three-dimensional objects by laying down layers of material from a digital file. These layers can be seen as a thinly sliced cross-section of the object.
3. CNC:
Computer Numerical Control or CNC uses a 3D solid model in computer-aided design to create a part through computer-controlled cutting and milling.
4. PolyJet:
Polyjet uses curable liquid polymers to create parts with thin and fine layers with complex details and full colour. It uses high-resolution ink-jet technology to produce parts economically by jetting layers of liquid photopolymer as thin as 16 microns (0.0006”).
5. Fabrication:
Fabrication refers to the process of creating a physical prototype or model of a design using various manufacturing techniques. This often involves the quick and precise production of a tangible representation of a product or part, allowing for testing, evaluation, and iteration before final production.
6. Lamination:
Lamination uses adhesive-coated paper, plastic, or metal laminates as a 3D printing. The sheets of material are stuck together, layer-by-layer, and cut into shapes with a knife or laser cutting.
7. Digital Light Processing:
Digital Light Processing or DLP is a 3D printing technology, which is used in producing photopolymer parts. Having similarities with Stereolithography or SLA, DLP becomes distinctive with just one but a significant difference – where SLA machines use a laser that traces a layer, a DLP machine uses a projected light source to cure the entire layer at once.
Here are the factors to consider in Rapid Prototyping:
1. Clearly Define Objectives:
Before you embark on a rapid prototyping journey, be crystal clear about what you aim to achieve. By setting clear objectives, you provide a roadmap, which ensures the end goal. Take time to brainstorm, gather insights, and outline your goals. This clarity will guide the rapid prototyping for product design and functionality, ensuring it resonates with your intended audience.
2. User-Centric Approach:
At the heart of a successful rapid prototyping process lies a user-centric approach. Your prototype isn’t just a representation of your idea; it’s a tool to understand user needs, preferences, and pain points. By prioritizing the user experience, you increase the likelihood of developing a product or solution that meets real-world needs and expectations.
3. Cost-Efficiency and Scalability:
While rapid prototyping emphasizes speed and agility, it’s essential to strike a balance between cost-efficiency and scalability. Assess your budget constraints, resources, and long-term goals to determine the most cost-effective prototyping methods without compromising quality.
4. Iterative Process and Flexibility:
Types of rapid prototyping thrive on iteration and flexibility. Recognize that your initial prototype won’t be perfect, and that’s okay. Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement, iterating based on feedback, testing results, and evolving requirements. Stay flexible and open-minded throughout the prototyping process.
Remember, rapid prototyping is about learning, adapting, and refining your concept iteratively.
5. Collaboration and Communication:
Last but not least, collaboration and communication are paramount in rapid prototyping. Cubein’s rapid prototyping solutions bring a diverse team with varied expertise, perspectives, and skills to foster creativity and innovation.
Rapid prototyping for product design is a powerful tool to transform ideas into tangible solutions quickly. By considering these five key factors, you can set the stage for a successful prototyping journey. Remember, the concept of rapid prototyping is as much about the process as it is about the result.
Visit Cubein to learn more about the types of rapid prototyping and other information.